The health of ecosystems on which we and all other species depend is deteriorating more rapidly than ever.
National Geographic Society and the Wyss Campaign for Nature are working together to inspire the protection of 30 percent of the planet by 2030. The future will be bad for us if we don’t act now. There is no future for us without nature.
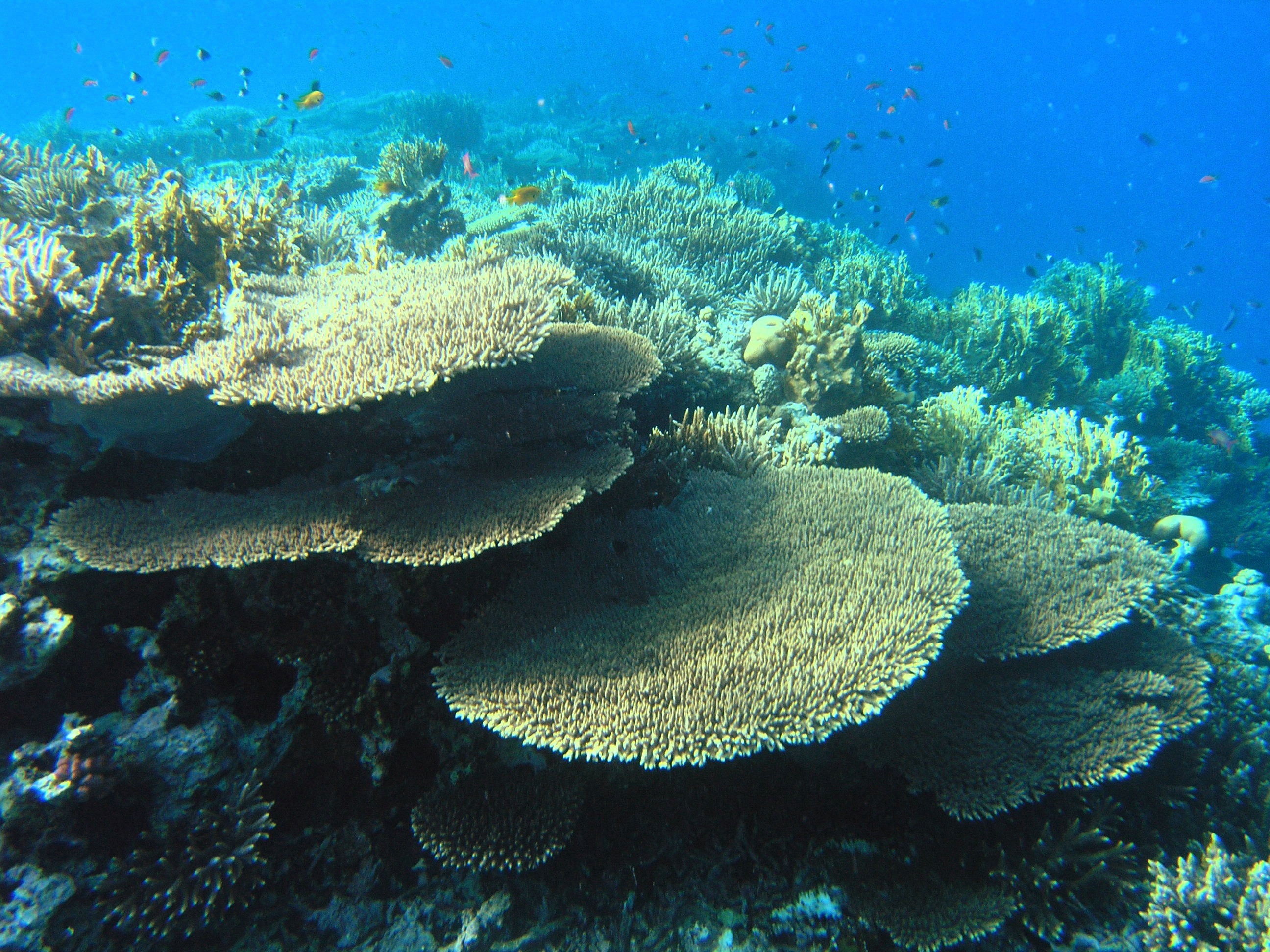
Air pollution affects ecosystems in a number of ways, altering basic ecosystem functions such as primary production (plant growth) and biogeochemical cycling which in turn affect the ecosystem services and therefore the benefits that humans get from the environment such as timber, clean drinking water and an appreciation of nature. The complex causal chains by which air pollution subsequently...
The health of ecosystems on which we and all other species depend is deteriorating more rapidly than ever.
National Geographic Society and the Wyss Campaign for Nature are working together to inspire the protection of 30 percent of the planet by 2030. The future will be bad for us if we don’t act now. There is no future for us without nature.
Air pollution affects ecosystems in a number of ways, altering basic ecosystem functions such as primary production (plant growth) and biogeochemical cycling which in turn affect the ecosystem services and therefore the benefits that humans get from the environment such as timber, clean drinking water and an appreciation of nature. The complex causal chains by which air pollution subsequently affects a range of ecosystem services have been reviewed extensively elsewhere, bringing together the evidence for these links.
Air pollutants such as sulfur may lead to excess amounts of acid in lakes and streams, and can damage trees and forest soils. Nitrogen in the atmosphere can harm fish and other aquatic life when deposited on surface waters. Ozone damages tree leaves and negatively affects scenic vistas in protected natural areas. Mercury and other heavy metal compounds that are emitted into the air from fuel combustion and deposited on land and in water accumulates in plants and animals, some of which are consumed by people.